Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMY60I8)
| Drug Name |
Cefixime
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CFIX; Cefixima; Cefiximum; Denvar; Necopen; Tricef; CL-284635; FK-027; FR-17027; Ofex (TN); Suprax (TN); Cefixime (JP15/USP/INN); (6R,7R)-7-({(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(carboxymethoxy)imino]acetyl}amino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(carboxymethyloxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7R)-7-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(carboxymethyl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino}-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6r,7r)-7-[-2-(2-amino-thiazol-4-yl)-2-carboxymethoxyimino-acetylamino]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-aza-b; 7beta-{(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(carboxymethoxy)imino]acetamido}-3-ethenyl-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
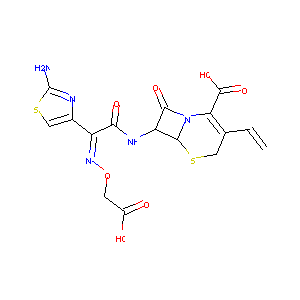 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 453.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Cefixime
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Cefixime (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Cefixime FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Genetics of chromosomally mediated intermediate resistance to ceftriaxone and cefixime in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Sep;53(9):3744-51. | ||||
| 7 | Transport characteristics of a novel peptide transporter 1 substrate, antihypotensive drug midodrine, and its amino acid derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jul;318(1):455-60. | ||||
| 8 | Flavonoids with epidermal growth factor-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity stimulate PEPT1-mediated cefixime uptake into human intestinal epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Oct;299(1):351-7. | ||||
| 9 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 10 | Duverne C, Bouten A, Deslandes A "Modification of cefixime bioavailabity by nifedipine in humans: involvement of the dipeptide carrier system." Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36 (1992): 2462-7. [PMID: 1489189] | ||||
| 11 | Product Information. CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil). Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 12 | Chrysos G, Gargalianos P, Lelekis M, Stefanou J, Kosmidis J "Pharmacokinetic interactions of ceftazidime and frusemide." J Chemother 7 Suppl (1995): 107-10. [PMID: 8904125] | ||||
| 13 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 14 | Brown G, Zemcov SJ, Clarke AM "Effect of probenecid on cefazolin serum concentrations." J Antimicrob Chemother 31 (1993): 1009-11. [PMID: 8360120] | ||||
